Anatomy of the penis and the natural erection process.
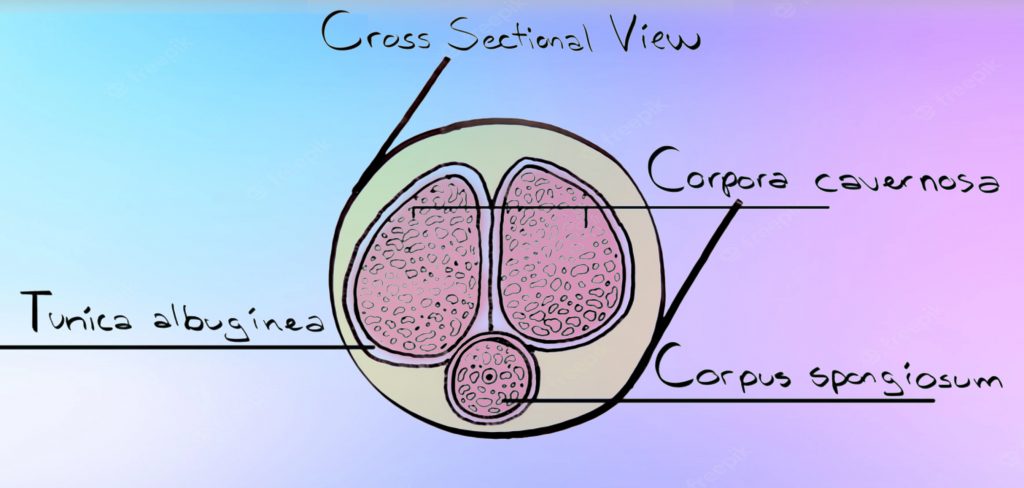
The body of the penis contains three cylindrical masses of tissue. The lower mass is the corpus spongiosum. The two top masses that the corpora cavernosal, which function as one entity and constitute the bulk of the penis. An elastic fiber sheath called the tunica albuginea surrounds all three masses.
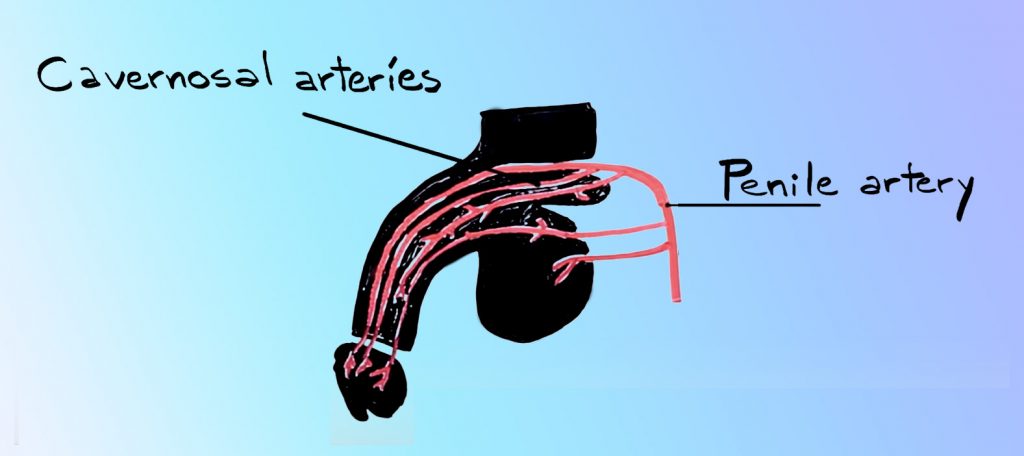
A cross-section cut of each cylinder looks like a sponge because of the hollow lacunar spaces. The Fill with blood During an erection, blood is supplied to the penis via the penile artery that splits into cavernosal arteries, which provide blood flow to each corpus cavernosal. The urethral artery provides blood to the corpus spongiosum. Helisine arteries then carry blood throughout the three cylindrical masses. Blood drains from the penis by the superficial deep dorsal cavernosal and crewel veins.
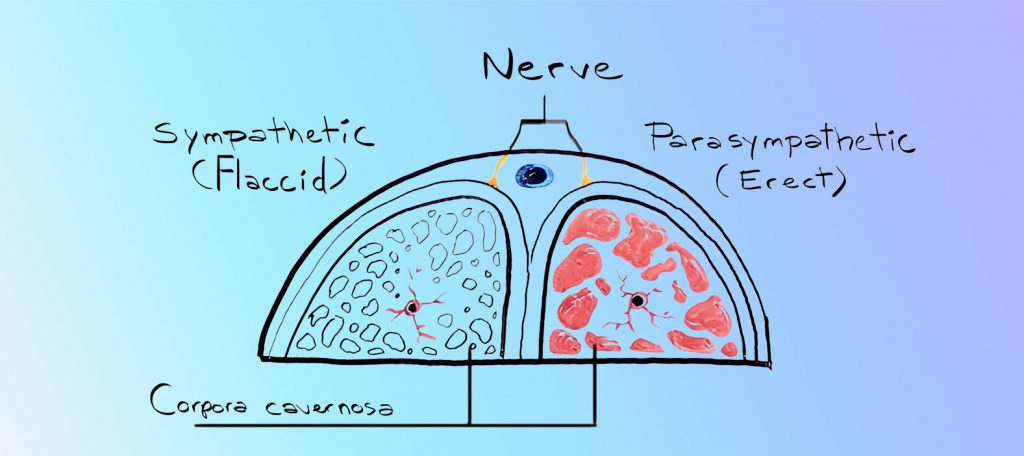
Sympathetic nerve stimulation results in the contraction of erectile tissue, which inhibits blood flow into the penis and causes the penis to become flaccid. Alternately, parasympathetic stimulation resulted in the relaxation of erectile tissue, which allows the lacunar spaces to fill with blood, resulting in an erection.
The erection process begins when the brain processes various types of stimuli that are sent down the spinal cord to the sacral plexus, which communicates with penile parasympathetic nerves to release acetylcholine. Acetylcholine causes endothelial cells with erectile tissue to release nitric oxide, the key messenger in initiating and maintaining an erection. Nitric oxide stimulates guanylate cyclase to convert guanosine triphosphate to cyclic guanosine monophosphate or cyclic GMP. Cyclic GMP decreases intracellular calcium stores within the cells of the corpora cavernosal, resulting in smooth muscle relaxation.
As the erectile tissue relaxes, the lacunar space is widened and becomes engorged with blood. As the tissue swells, it expands against the tunica albuginea, which presses against drainage venules, thus limiting blood flow out of the penis. As blood continues to flow into the penis, pressure increases, resulting in a rigid erection.